Contents
Quick Summary: Is welding automation suitable for your manufacturing needs? This guide delves into the types of welding applications best suited for automation, factors to consider before implementation, and comparisons with other welding methods. Equip yourself with the knowledge to make an informed decision
In the right applications, automated welding can substantially improve the quality, productivity, and profitability of manufacturing operations. Despite this potential, the welding process is often overlooked or ignored while manufacturers integrate various other forms of automation into their processes. As welding automation technologies continue to become increasingly efficient, versatile, and affordable, having an understanding of them can help a manufacturing company remain competitive.
Below, we provide an overview of automated welding, outlining what it is, what benefits it offers, what applications it is used in, how to determine if it is right for you, and how it compares to other welding methods.
What is Automated Welding?
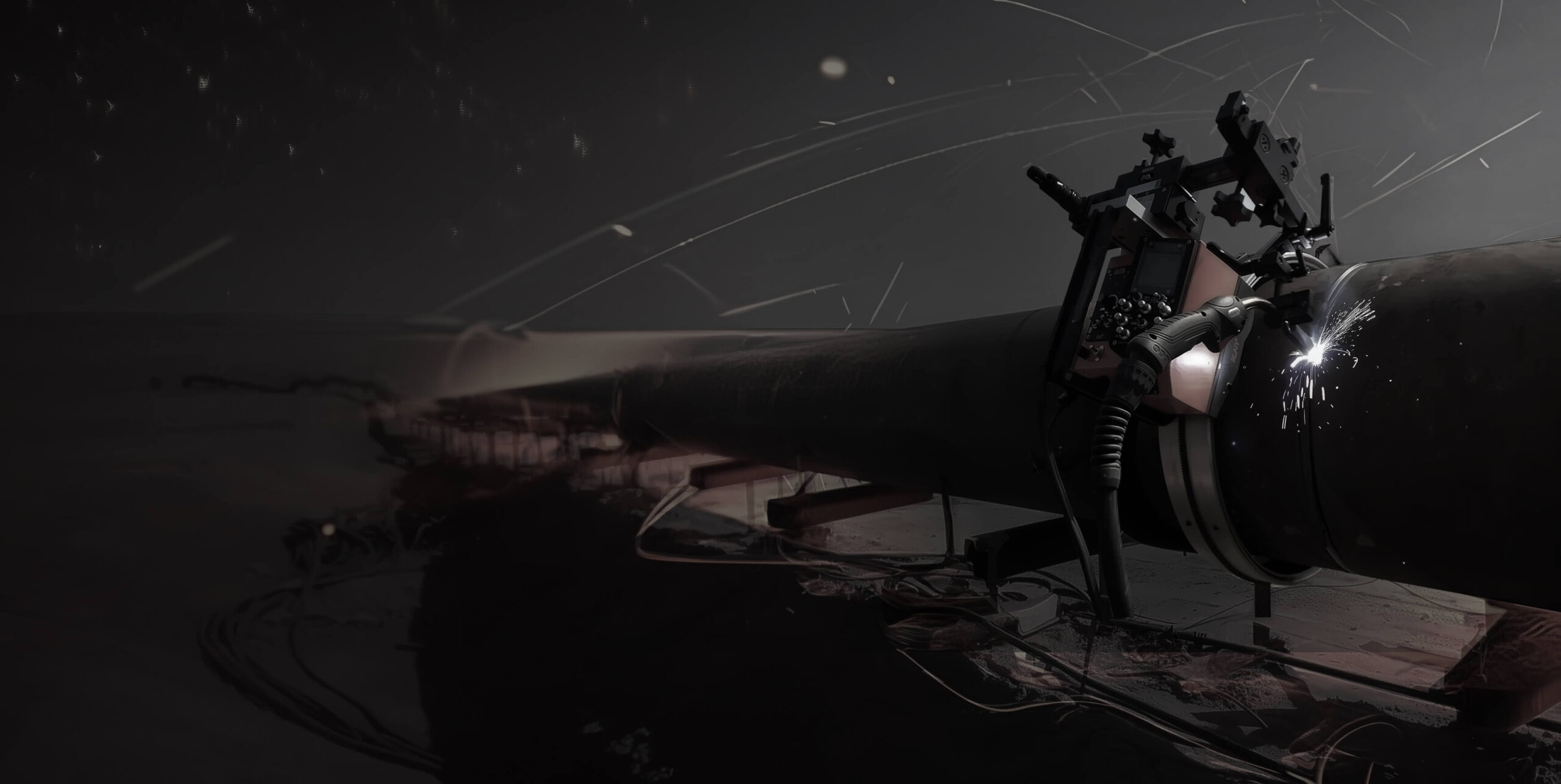
 Automated welding is a form of automatic welding that uses electronically controlled tools and equipment to handle and welding applications with minimal human oversight. Interfaced with the welding power supply and wire feeders, the tools and equipment allow for precise manipulation of each welding parameter and close monitoring of weld performance. This level of precision and control can improve productivity, reduce defects, and decrease overall production costs. Typically, the process is used in easily repeatable processes with high volume.
Automated welding is a form of automatic welding that uses electronically controlled tools and equipment to handle and welding applications with minimal human oversight. Interfaced with the welding power supply and wire feeders, the tools and equipment allow for precise manipulation of each welding parameter and close monitoring of weld performance. This level of precision and control can improve productivity, reduce defects, and decrease overall production costs. Typically, the process is used in easily repeatable processes with high volume.
Benefits of Automated Welding
When implemented properly, automated welding technologies provide a number of benefits, including the following:
- Better quality: Through accurate torch positioning, precise part motions, and electronic recall of input parameters, automated systems can significantly improve weld quality and weld uniformity.
- Greater capacity: Allows for higher productivity through increase arc-on-time, higher deposition rates and less weld stops and starts.
- Lower costs: With their increased working capacity, automated welding systems allow for much lower costs per weld relative to manually controlled processes.
- Safer working conditions: Automated welding systems create a safer work environment by distancing operators from the heat and fumes generated during the welding process.
- Reduced scrap costs: Tightly controlled weld parameters and part placement can improve accuracy and reduce scrap and rework costs.
- Decreased variable labor costs: Automating repetitive or challenging welding processes can significantly increase production outputs while decreasing variable labor costs.
Applications for Automated Welding
 Automated welding finds use in the manufacturing applications of a wide range of industries. For example:
Automated welding finds use in the manufacturing applications of a wide range of industries. For example:
- In shipbuilding applications, it is used to construct and repair ship hulls and their internal elements (e.g., stiffeners).
- In tank building applications, it is used to fabricate tank floors and external shells.
- In infrastructure applications, it is used to build bridges and bridge elements, hydroelectric dams, and penstocks.
- In military applications, it is used to make the exterior of nuclear submarines and spacecraft and other large structures with repeatable, long seams.
- In general fabrication applications, it is used to create a variety of parts and products, from small-scale pipe systems to tanks for fire extinguishers.
- In power generation applications, it is used for the construction of various elements in hydroelectric dams, nuclear power plants, and other power generation facilities, such as steam kettles and piping systems.
The above list is not all-inclusive. In addition to those listed above, automated welding systems can be employed in the manufacturing operations of many other industries. Depending on the requirements of the application, they can be utilized as standalone machines or integrated into larger, interconnected automation processes that handle material flow, assembly, and other operational aspects. The appropriate level of automation depends on the complexity of the parts being welded as well as the facility’s available resources and desired production volume and speed.
Automated Welding vs. Mechanized Welding vs. Robotic Welding
Welding automation technology can be split into three general categories, each of which offers a different level of automation and sophistication.
- Automated Welding: All welding parameters are electronically controlled, and manual adjustments are made prior to starting the process. Human operator tasks include programming and starting the machine, occasionally supervising the process, and troubleshooting when necessary.
- Mechanized Welding: Weld parameters are mechanically or electronically controlled, and manual manipulations are performed between welding operations to maintain the appropriate welding position. The machine handles the movement of the arc while the operator observes and makes any necessary adjustments.
- Robotic Welding: A robot is programmed to perform the welds while the operator maintains responsibility for quality control and addresses any deviations or issues during the process. This process is well-suited for complex welding applications, such as the precision micro-welding of small parts used in electronic or automobile applications.
Is Welding Automation Right for my Application?
Before investing in an automated welding system, it is vital to make sure your welding operation is a good candidate for automation. Some of the factors to consider to help guide your decision include:
- Types of Welding Application: While basic automated welding systems are great for performing simple and repetitive welds at high speeds, joining parts with gaps or hard-to-access locations may present some challenges. An automated welding solutions provider can evaluate a blueprint of the part and determine if the welding equipment can be configured accordingly.
- Production Volume: Since one of the key benefits of welding automation is the ability to quickly perform high volumes of welds, it is important to make sure your facility’s production volume is large enough to justify the investment cost.
- Operator Skill: It is important to keep in mind that an experienced welder will be required for programming, troubleshooting, and recalibrating the system as needed.
Based on current trends in the welding industry, the growth of automated welding is expected to continue as companies seek to improve the efficiency, safety, and profitability of their operations even further. In response to this rising demand, automated systems are becoming increasingly more precise, affordable, and accommodating of smaller-volume applications and unique welding requirements.
Contact the Gullco Experts for Your Welding Automation Needs
A well-implemented welding automation solution can dramatically improve quality, efficiency, and worker safety while reducing operational costs and material waste. If you’re looking to automate your welding operations, turn to the experts at Gullco International! We are a premier manufacturer and distributor of welding automation technology. For additional information about our offerings, check out our product catalog. To learn more about automated welding and how it can benefit your operations, contact us today.
Relevant Resources


Frequently asked questions
Find quick answers to your questions here, ask our AI assistant, or contact us for any additional inquiries.
Gullco’s automation solutions can be tailored to fit most applications. Our products are designed for flexibility and customization. To determine the best approach for your needs, please provide some details about your project. We’re happy to discuss how we can help you achieve optimal results.
Thanks for your interest in Gullco products! For accurate pricing and to discuss your specific needs, we recommend you Request a Quote and your local distributor will promptly respond.
Gullco International has presence worldwide. To locate the distributor in your area, visit our distributor locator and choose your region and location.
Absolutely! We’d be happy to schedule a product demonstration for you. Please let us know which product(s) you’re interested in and your preferred date and time, and we’ll get that arranged. We look forward to showing you how Gullco can improve your operations.
You can locate your product manual in our Resource library.
That’s a great question! We’re really proud of the ruggedness of our Gullco products. A big part of it comes from our commitment to North American manufacturing. We’ve invested over $12 million in state-of-the-art CNC equipment to ensure precision and durability. Plus, we do most of the manufacturing in-house, which gives us tight control over quality.
Ready to get started?
With over seven decades of experience and a worldwide reach, we synthesize the skills, knowledge, and experience to offer reliable, innovative solutions to automate welding and associated processes. We are committed to continual improvement, developing new welding automation systems and equipment to address the ever-changing needs of the industry.